The last few months have been a watershed for the digital payments space in India. With concerted efforts from the government, as well as businesses, the landscape has seen some tectonic developments. From mobile wallets to lower cost, interoperable solutions such as UPI, Bharat QR code and Aadhar Pay, more tailor-made solutions to meet specific needs of small businesses and mass consumer segments are now seen on the horizon. Moreover, with the government announcing a budget of Rs. 495 crore to promote digital transactions using BHIM (a UPI enabled app), with a target to catalyze 25 billion digital transactions in the fiscal year ending March 2018, policy and market forces are colluding to promote a less cash economy. However, despite recent advancements, the consumption spends using digital means currently stand at a dismal 51%, making it crucial to investigate the reasons for low solution adoption.
For India to accelerate its progress towards a less cash economy, there is a clear need to deliberate on economic, social and behavioral dependencies that steer the decision of the low-income population to adopt digital transactions. In that context, Catalyst, an initiative to accelerate adoption of digital payments in India, has formed strategic partnerships with research organisations such as People Research on India’s Consumer Economy (PRICE), IFMR LEAD, CEGA and Ideas 42. Bringing in strong research expertise and rich insights to bear on Catalyst initiatives, these partnerships will play a substantive role in guiding Catalyst�s engagements with operational partners to design and implement a range of needs-based payment solutions for the �last mile”. They will help us get a deeper understanding on how merchants and consumers interact with financial tools, what are the barriers and what are the value propositions that induce them to transact digitally
Jaipur, Catalystaic first Digital Payment Lab
Adopting a unique ecosystem approach defined by local geography, Catalyst has operationalized its very first digital payments lab in Jaipur – a tier 2 city with a 3 million plus population, more than 200,000 commercial establishments, and over 75,000 informal establishments including home based and roving businesses. Using new technologies, business models, and institutional innovations, combined with rigorous research evidence, Catalyst aims to build an inclusive digital financial ecosystem in Jaipur – one that is demand-driven, accessible and serves as a foundation for greater financial inclusion. Our goal is to create a template for implementing similar initiatives in other cities.
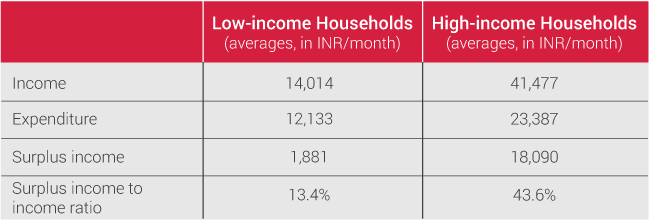
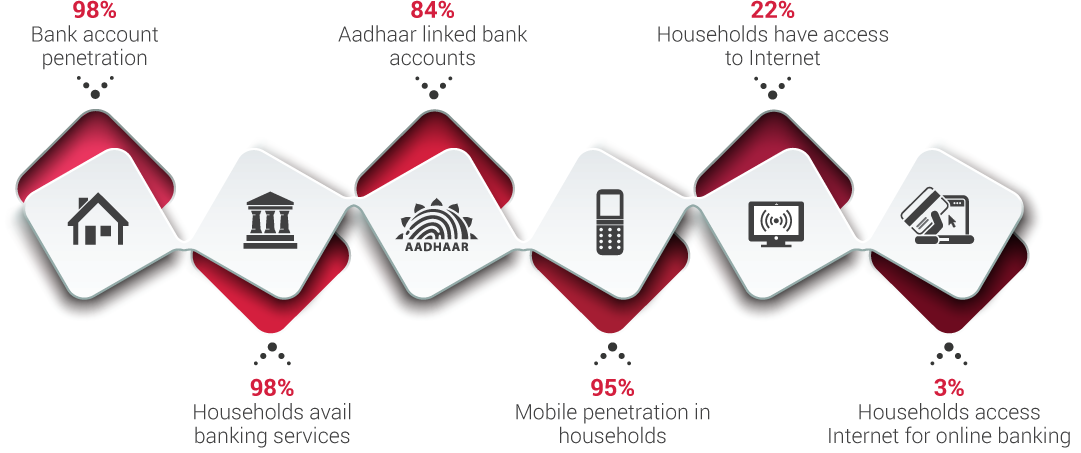
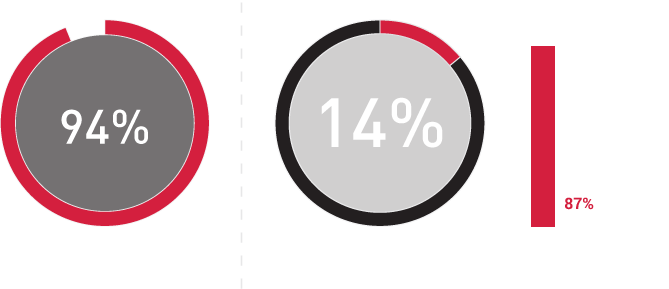
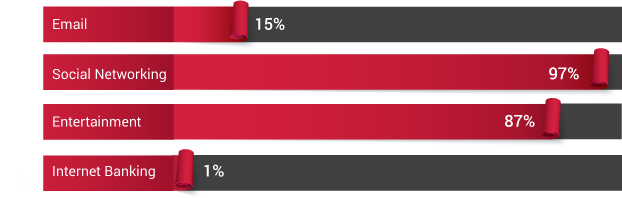
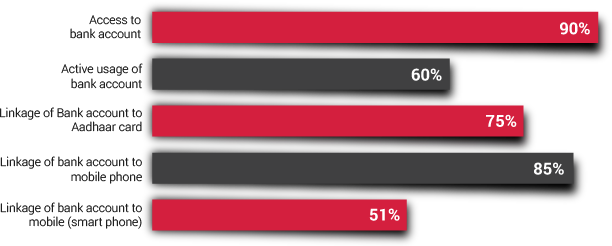
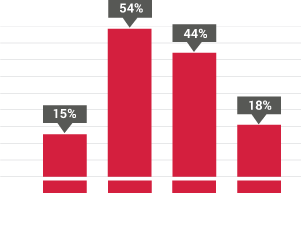
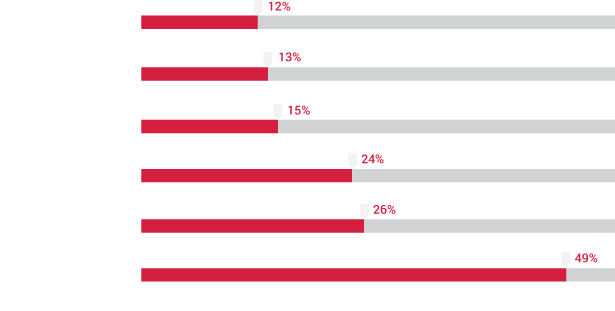
Before embarking on this challenging journey to transform Jaipur into a less cash economy, we immersed ourselves in the current financial and socio-economic landscape of Jaipur, and particularly focused on understanding merchant perspectives towards digital payments. The Sixth Economic Census conducted in Rajasthan (May-June2013), as well as the �Jaipur Population Profile� study conducted by PRICE, helped us in getting an understanding of the city across various themes, such as income segments, occupational categories, bank penetration, expenditure, saving, investments and use of digital technologies. In addition to providing an overview of the income segments of Jaipur, which is critical for solution design and implementation, the latter also enabled us to assess the digital readiness in communities, looking into different aspects of technology � particularly, access, usage and prevalent infrastructure. Insights from these two studies have underpinned further exploratory initiatives to decode the market dynamics of Jaipur city.